The Good and the Bad of Node.js Web App Development
Being the most popular programming language, JavaScript is also one of the most universal software development technologies. Traditionally used as a web frontend development tool, it has also become a major cross-platform mobile development tool as a basic technology for a large number of platforms, such as Apache Cordova/PhoneGap, React Native, NativeScript, Appcelerator Titanium.
But the areas of application for JavaScript do not end here. Lately, there has been a lot of buzz around the use of JavaScript for server-side programming. One of the tools that indicated this shift in web development was Node.js.
What is Node.js?
Node.js is actually not a framework or a library, but a runtime environment, based on Chrome’s V8 JavaScript engine.
The technology was first introduced back in 2009 by Ryan Dahl at the annual European JSConf and was immediately recognized as “the most exciting single piece of software in the current JavaScript universe”.
As an open-source project, Node.js was sponsored by Joyent, a cloud computing and hosting solutions provider. The company invested in a number of other technologies, such as the Ruby on Rails framework, and provided hosting services to Twitter and LinkedIn. The latter also became one of the first companies to use Node.js for its mobile application backend. The technology was later adopted by a number of technology leaders, such as Uber, eBay, Walmart, and Netflix, to name a few.
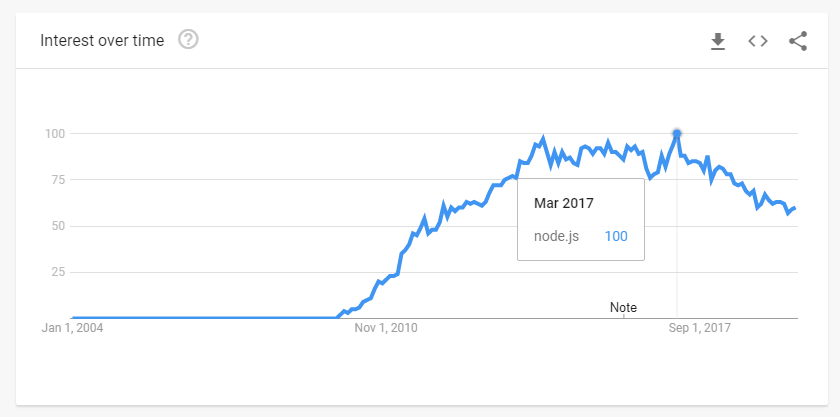
However, it wasn’t until recently that wide adoption of server-side JavaScript with Node.js started. The interest in this technology peaked in 2017, as per Google Trends, and remains high.
Node.js downloads. Install Long-Term Support and the latest versions of Node.js for Windows and macOS here. Also, a reminder – npm is distributed with Node.js out-of-the-box.
Documentation. Find the docs and getting started guides at the link.
Node.js IDEs. Almost any popular code editor has support and plugins for JavaScript and Node.js, so it only matters how you customize your IDE to your coding needs. But, many developers highly praise special tools from VS Code, Brackets, Atom, and WebStorm.
Frameworks. Using middleware over pure Node.js is a common practice that makes developers’ lives easier. We have a separate article comparing popular Node.js frameworks, where we look at Express.js, Meteor, Sales.js, Koa.js, Keystone.js, and Loopback.js.
For more JavaScript ecosystem tools used with Node.js, see the dedicated article.
Node.js strengths and weaknesses make it the subject of a heated discussion. To set the record straight, we have analyzed both – Node.js pros and cons – in an attempt to find out what projects can benefit from this technology choice. So, why use Node.js?
The Benefits of Node.js
⊕ Robust technology stack
JavaScript has proven to be an undisputed leader among the most popular programming languages. In turn, Node.js has become a stand-alone name in the industry. With a total of 368,985,988 downloads and over 750 new contributors as stated in the Node-by-numbers report 2018, the project seems to be stronger than ever.
Using Node.js for backend, you automatically get all the pros of full-stack JavaScript development, such as:
- better efficiency and overall developer productivity
- code sharing and reuse
- speed and performance
- easy knowledge sharing within a team
- a huge number of free tools
Consequently, your team is a lot more flexible, the development is less time-consuming and as a result, you get fast and reliable software. Developers trained in frontend JavaScript can start programming the server side with minimum effort. With the same language on both sides, you can reuse code on the frontend and the backend by wrapping it into modules and creating new levels of abstraction.
Despite a common belief, being a full stack developer you are in no way limited to the traditional MEAN (MongoDB, Express.js, AngularJS, and Node.js) stack. The only must-have in this case is Node.js (there is no alternative in JavaScript for backend programming). The rest of the technologies within this stack are optional and may be replaced with some other tools providing similar functionality (read about the alternatives in our separate article).

⊕ Fast-processing and event-based model
Node.js is fast; it is not a myth. Take a look at the performance tests by toptal.com, comparing how GO, PHP, Java, and Node.js handle concurrent requests. There a couple of reasons for Node.js showing such results:
V8 engine. The engine used in Node.js implementation was originally developed for the Chrome browser. Written in C++, Chrome’s V8 is used to compile functions written in JavaScript into machine code, and it does the job at an impressive speed. Just check performance benchmarks in V8’s blog. Thanks to Google investing heavily in its engine, V8 demonstrates performance improvements every year, and Node.js extracts the whole bag of benefits out of it.
Non-blocking Input/Output and asynchronous request handling made Node.js capable of processing requests without any delays. In the context of backend, synchronous processing assumes that code is executed in a sequence. Thus, each request blocks a thread, making other requests wait for it to be finished. Asynchronous processing allows requests to be processed without blocking (non-blocking I/O) the thread. So after a request is processed, it can push out a callback and continue serving requests. That helps Node.js make the most of single threading, resulting in short response time and concurrent processing.
Another aspect is the event-based model. When using a common language for both client/server-side, synchronization happens fast, which is especially helpful for event-based, real-time applications. Due to its asynchronous, non-blocking, single-threaded nature, Node.js is a popular choice for online gaming, chats, video conferences, or any solution that requires constantly updated data.
The examples speak for themselves: many leading companies switched technologies to developed Node.js applications and noticed significant improvements – PayPal, for instance, noticed a 35 percent decrease in response time since migrating from Java.
⊕ Scalable technology for microservices
Since it’s a lightweight technology tool, using Node.js for microservices architecture is a great choice. This architectural style is best described by Martin Fowler and James Lewis as “an approach to developing a single application as a suite of small services, each running in its own process and communicating with lightweight mechanisms, often an HTTP resource API.”
Accordingly, breaking the application logic into smaller modules, microservices, instead of creating a single, large monolithic core, you enable better flexibility and lay the groundwork for further growth. As a result, it is much easier to add more microservices on top of the existing ones than to integrate additional features with the basic app functionality.
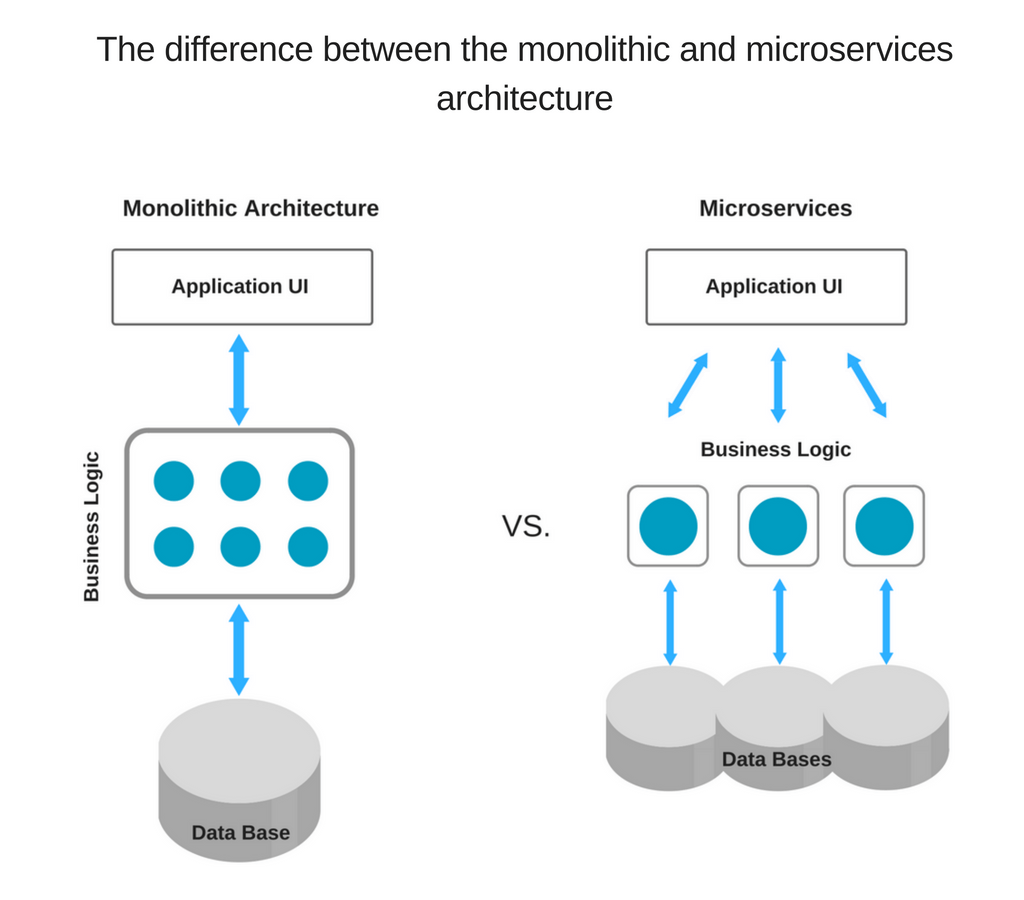
Monolithic architecture vs microservice architecture in a nutshell
Node.js is the technology of choice when building and deploying microservices ecosystem solutions, according to Node.js User Survey Report 2017. About half of the respondents are using microservice-related technologies (namely, Docker, the leading software containerization platform) to build Node.js web apps:
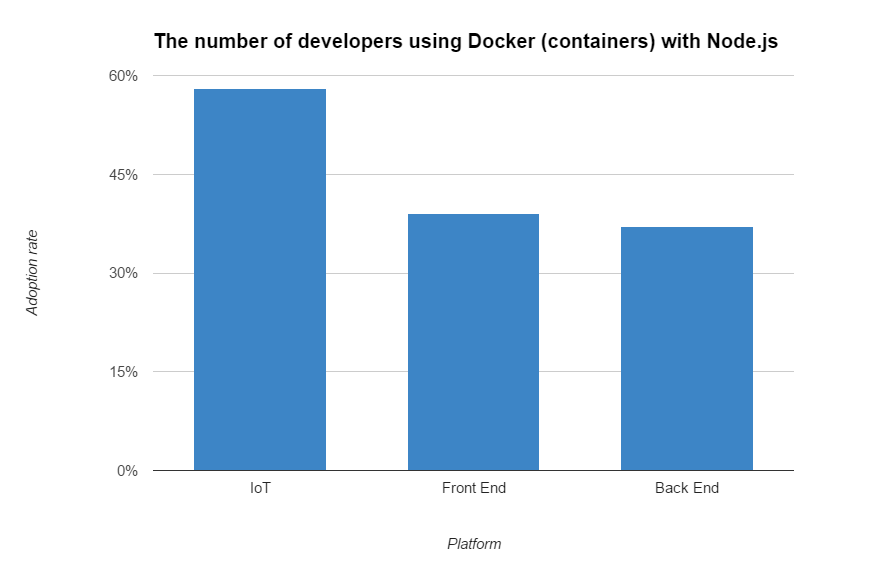
Percentage of developers using Docker containerization with Node.js
More recent findings show that microservice-related technologies such as Docker and Kubernetes experienced growth in usage in 2018, as this architectural style gets only more popular. With each microservice communicating with the database directly through streams, such architecture allows for better performance and speed of application. A match made in heaven is supported by two frameworks widely used for microservice architecture. The Express framework lists IBM and Uber among its users, while rectify is used by npm and Netflix.
As an example of live implementation, Walmart’s shift to microservices architecture with Node.js resulted in the following immediate benefits:
- Overnight 20 percent conversion growth in general and 98 percent mobile conversion growth
- One hundred percent uptime on Black Friday (handling over 500 million page views)
- Saving up to 40 percent on hardware and 20-50 percent on overall operations
Another bright example of how Node.js can outperform the competition in terms of performance is the case of GoDaddy. Running the SuperBowl ad campaign, the company was able to handle 10.000 requests per second with out downtime, using only 10 percent of the hardware thanks to Node.js.
⊕ Rich ecosystem
One word – npm, a default Node.js package manager, also serves as a marketplace for open-source JavaScript tools, which plays an important role in the advance of this technology. With about 836,000 libraries available in the npm registry as of now, and over 10,000 new ones being published every week, the Node.js ecosystem is quite rich. The same stats point out that 97 percent of modern web applications consist of npm modules. And that’s proof of its undisputable popularity among developers.
With such a vast variety of free tools accessible in a few clicks, there is a huge potential for the use of Node.js. At the same time, open-source software enjoys growing popularity as it allows you to build new solutions reducing the overall costs of development and time to market.
⊕ Strong corporate support
As mentioned above, the development of Node.js was supported by Joyent. In 2015, the Node.js Foundation was created to “enable widespread adoption and help accelerate the development of Node.js.” IBM, Microsoft, PayPal, Fidelity, and SAP became the founding members of the organization.
The list of organizations using Node.js in production is constantly growing. It currently includes almost three hundred well-known companies, such as PayPal, Medium, Trello, Uber, and Zendesk.
Very few open source projects have ever enjoyed such strong support from the world’s leading companies. And that foretells Node.js has outstanding potential.
⊕ Seamless JSON support
Although other backend technologies like PHP and Ruby on Rails can use JSON format for communication, Node.js does it without converting between binary models and uses JavaScript. This is especially handy when you need to build RESTful APIs for NoSQL database support, like MongoDB – the letter M in the MEAN stack. This seamless communication with one of the main data transfer standards is another advantage of the JavaScript ecosystem.
The Drawbacks of Node.js
Θ Performance bottlenecks with heavy computation tasks
The biggest drawback of Node.js even now is its inability to process CPU bound tasks. But, to understand what the roots of this issue are, we need a little bit of context. Let’s begin with the basics, with JavaScript itself.
As we know, Node.js is a runtime environment that executes JavaScript on the server side. Being a frontend programming language, JavaScript uses a single thread to process tasks quickly. Threading is not required for it to work, because tasks in JavaScript are lightweight and take little CPU.
Turning back to Node.js, now we know why it is considered single threaded: It processes JavaScript, which is single threaded. A non-blocking input/output model means that Node.js answers the client call to start a request and processes the task during the time it shoots callback, as the task is ready. Processing tasks asynchronously, Node executes JS code on its single thread on an event basis. That is what called an event-loop.
The problem occurs when Node.js receives a CPU-bound task: Whenever a heavy request comes to the event loop, Node.js would set all the CPU available to process it first, and then answer other requests queued. That results in slow processing and overall delay in the event loop, which is why Node.js is not recommended for heavy computation.
However, in 2018, multithreading was introduced in Node.js as an experimental feature with the 10.5.0 update. A new feature called worker threads module can be used to leverage additional threads from a thread pool, to carry CPU bound tasks. But that can be done only on machines with multiple cores, as Node.js still allows you to use one core for one thread. That means that heavy parallel processes can be executed on a different thread. This feature is remaining experimental in Node.js version 12 but has been significantly improved.
Θ Callback hell issue
Due to its asynchronous nature, Node.js relies heavily on callbacks, the functions that run after each task in the queue is finished. Keeping a number of queued tasks in the background, each with its callback, might result in the so-called callback hell, which directly impacts the quality of code. Simply put, it’s a “situation where callbacks are nested within other callbacks several levels deep, potentially making it difficult to understand and maintain the code.”

Example of code with nested callbacks
Image source: callbackhell.com
Yet, this is often considered a sign of poor coding standards and lack of experience with JavaScript and Node.js in particular. The code, represented above, can be refactored and simplified, in just a few steps, as shown at callbackhell.com.
Θ Immaturity of tooling
Although the core Node.js modules are quite stable and can be considered mature, there are many tools in the npm registry which are either of poor quality or not properly documented/tested. Moreover, the registry itself isn’t structured well enough to offer the tools based on their rating or quality. Hence it might be difficult to find the best solution for your purposes without knowing what to look for.
The fact that the Node.js ecosystem is mostly open source, has its impact as well. While the quality of the core Node.js technology is supervised by Joyent and other major contributors, the rest of the tools might lack the quality and high coding standards set by global organizations.
Θ Growing demand for experienced professionals
Despite a common belief, not all JavaScript developers are Node.js developers as well. Mastering server-side JavaScript programming requires a significant amount of effort and a certain background in backend development. Due to such a steep learning curve, the number of Node.js engineers is significantly lower than the total number of JS professionals.
As the hype over Node.js continues to grow, the demand for experienced professionals in this field increases.
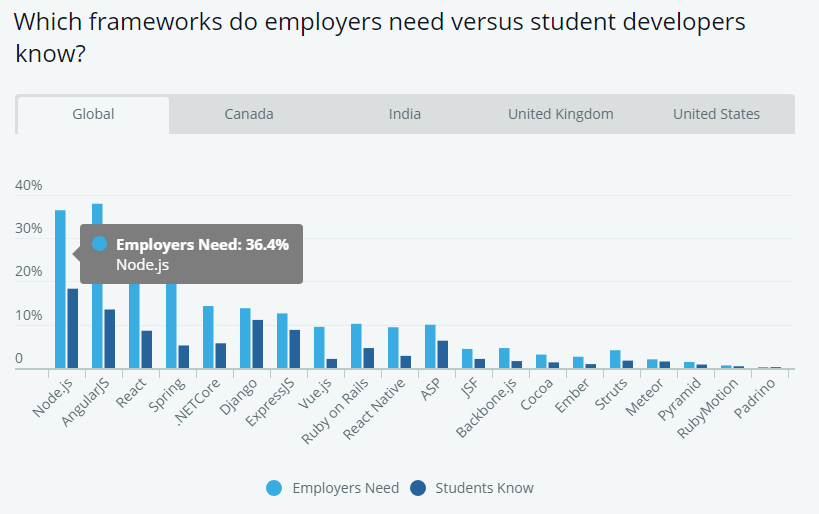
There’s a big knowledge gap between engineering students starting on their jobs and employers’ needs
Source: HackerRank
Thus, with millions of JavaScript developers out there, it might be hard to find a skilled Node.js professional for your project. In this case, you certainly don’t want to limit your search to only one country. Sourcing technical talent overseas has long become the norm in the IT industry.
How to Learn Node.js
Here’s your starter pack to understanding and working with Node.js.
Turorials. Don’t limit yourself to official docs: See tons of free lessons on W3Schools, visit international workshops from Nodeschool, and of course, use the library of free tutorials by freeCodeCamp.
Classes. If you’re a dedicated student, start an online course on Node.js: Here’s one on PluralSight, and of course, one on Udemy.
Interactive learning. See free and paid resources that allow you to learn Node.js using interactive lessons and exercises. One of the most popular is The Art of Node.
Community. See the official list of community-run Node.js projects. A quick tip: Research Facebook groups and communities in your area/first language. And of course, refer to the Node.js communities on Reddit, a tag on StackOverflow, and the topic on Quora.
Node.js vs Ruby on Rails vs Django vs Symfony
There’s not a lot of technologies that can compete with Node.js’ popularity or market demand. However, if we look at the alternatives for server-side programming, we see at least three more shining stars in the sky. It’s Ruby on Rails, Django, and Symfony. Let’s see whether they hold up to Node.js’ benefits and share its drawbacks.
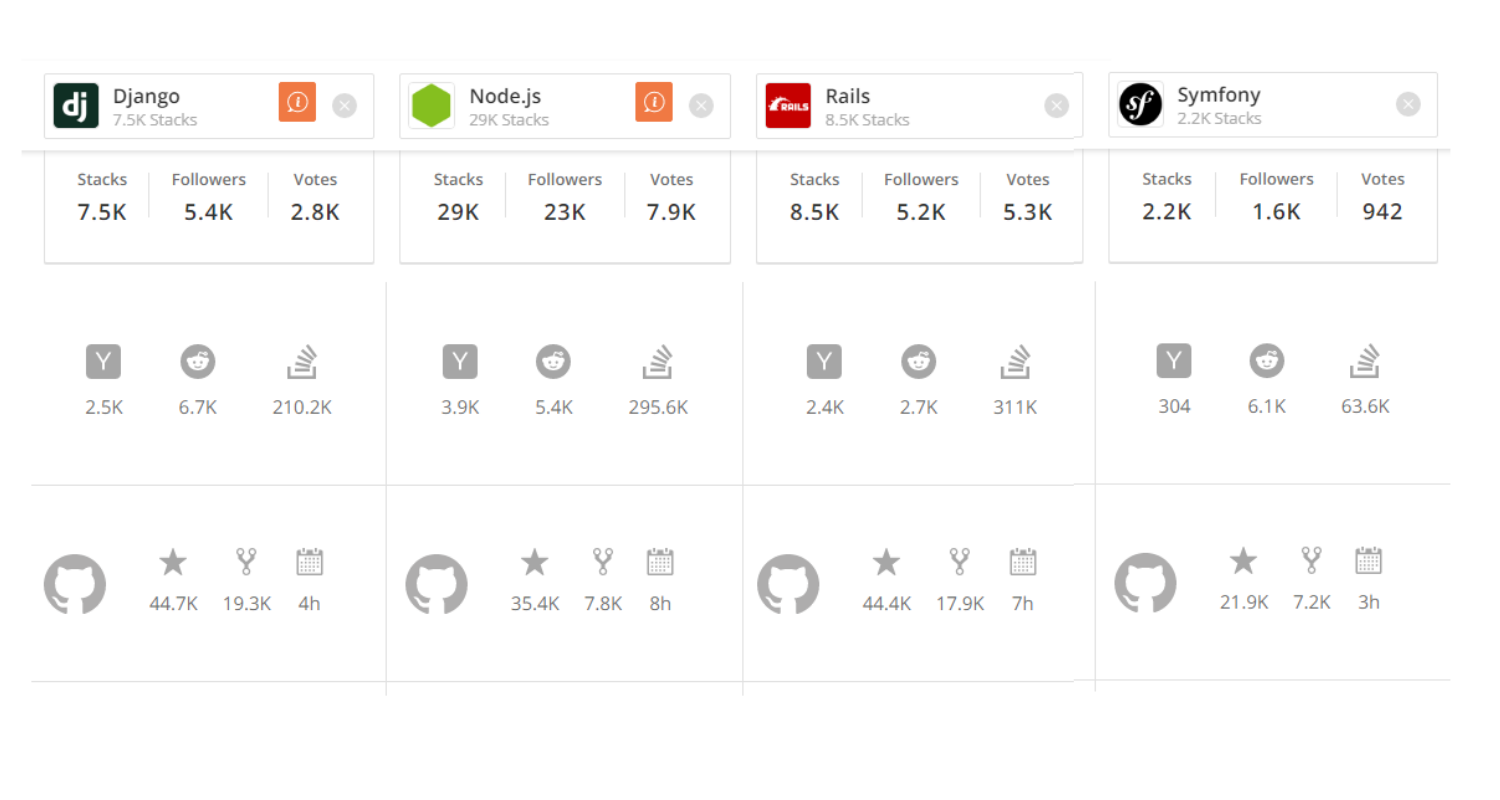
Comparing Node.js, Rails, Django, and Symfony stats
Source: StackShare
Ruby on Rails is known for its simple but opinionated language and the availability of gems – Rails’ own ecosystem of custom packages. Ruby itself is an intuitive and beginner-friendly language with a supportive and dedicated community that contributes code to RubyGems. Rails was created for rapid development and prototyping, though it’s successfully used by such brands as GitHub, Twitter, and Airbnb, proving its wide range of use cases. Its data migration functionality is especially impressive – unlike Node.js, which uses additional packages, Rails already has a feature allowing you to easily and consistently manipulate your database.
When should you use Rails over Node.js? Rails can’t compete with Node’s performance and scalability, however, Rails can be a better choice for fast development. Node.js does have to use third-party modules to achieve that speed of development, but Ruby has it all unconventionally. As for the language, no tool has a distinct advantage – while Node.js has a high demand but low proposition, Ruby’s talent pool is initially smaller.
Django is a web framework on Python, the fastest growing programming language according to the data on StackOverflow. Marketed as a tool for perfectionists with deadlines, it’s created to make applications as fast as possible and in the most structured, secure, and easy to understand way. Django, along with Python, is also considered to have a milder learning curve. While working with Node.js will require extensive knowledge of JavaScript, Django is a “batteries included” technology. It has a built-in admin panel to easily update and maintain your databases and templates to accelerate your work.
When should you use Django over Node.js? Compared to Node.js, Django is a beginner-friendly tool. Other than the language itself, there’s no real reason to choose one over the other. It’s more of a question about your comfort and experience with either JavaScript or Python than the specific use cases.
Symfony is a PHP framework which automatically provides it with 20+ years of documentation, and a massive, active community. More than 80 percent of the web is powered by PHP with projects like Facebook, Baidu, or any other website running on WordPress. While Symfony is just one of PHP frameworks on the market, it’s impressively stable, scalable, and works well for large-scale projects. It also uses a templating engine Twig that works akin to many PHP-based Content Management Systems.
When should you use Symfony over Node.js? Symfony naturally supports CMSs features such as templates and admin dashboards which allows it to run blogs, news sites, and eCommerce stores. Some of the examples include Yahoo Answers, Dailymotion, and National Geographic.
Make Node.js Shine
Obviously, with all the listed Node.js advantages and disadvantages, the technology is no silver bullet. But neither is Java, .Net framework or PHP. Yet, there are specific cases where each one of the listed technologies perform best. For Node.js, these are real-time applications with intense I/O, requiring speed and scalability.
This might be social networks, gaming apps, live chats or forums as well as stock exchange software or ad servers, where speed is everything. Fast and scalable, Node.js is the technology of choice for data-intensive, real-time IoT devices and applications.
Node.js made JavaScript a full-stack technology of choice for web application development. Due to its non-blocking architecture, Node.js works well for encoding and broadcasting video and audio, uploading multiple files, and data streaming. The latter might be exceedingly useful for Travel industry software where you need to source data from different APIs of different suppliers.
Recently, Node.js has been actively used in enterprise-level software. While there is still much argument about this, many large companies and global organizations, such as Capital One and NASA, have already adopted Node.js. And the enterprise Node.js ecosystem continues to mature with such tools as IBM API Connect, Triton by Joyent, N|Solid by NodeSource, Red Hat OpenShift, Trace by RisingStack and others.

Comments
Post a Comment